Abstract
Objective
Aripiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic drug which is metabolized by the polymorphic enzyme cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6). The aim of the present study was to investigate the impact of the CYP2D6 genotype on serum concentrations of aripiprazole (ARI) and to determine the sum of ARI and the active metabolite dehydroaripiprazole (DARI) in psychiatric patients.
Methods
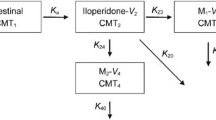
Data on steady-state serum concentrations and the CYP2D6 genotypes of patients treated with ARI were extracted from a routine therapeutic drug monitoring database. The 62 patients included in the analysis were stratified into the following subgroups according to CYP2D6 genotype: *1/*1 (homozygous extensive metabolizers, EMs; n = 37), *1/*3–6 (heterozygous extensive metabolizers, HEMs; n = 17) and *3–6/*3–6 (poor metabolizers, PMs; n = 8). Dose-adjusted serum concentrations (C/D ratios) of ARI and ARI + DARI were compared between the subgroups.
Results
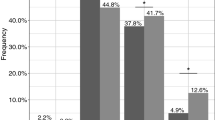
The median serum concentration of ARI was 1.7-fold higher in PMs than in EMs (45.5 vs. 26.3 nM/mg, p < 0.01). The observed serum concentration of the active sum of ARI + DARI was 1.5-fold higher in PMs than in EMs (53.9 vs. 37.0 nM/mg, p < 0.05). Numerical differences in serum concentrations between HEMs and EMs were less pronounced, but statistically significant for both ARI (p < 0.05) and ARI + DARI (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
The present study demonstrates that serum concentrations of both ARI and the active sum of ARI + DARI in psychiatric patients were significantly affected by CYP2D6 genotype. The observed differences in median C/D ratios indicate that PMs typically need 30–40% lower doses to achieve a similar steady-state serum concentration as EMs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirchheiner J, Nickchen K, Bauer M, Wong ML, Licinio J, Roots I, Brockmoller J (2004) Pharmacogenetics of antidepressants and antipsychotics: the contribution of allelic variations to the phenotype of drug response. Mol Psychiatry 9:442–473
Bertilsson L, Dahl ML, Dalen P, Al-Shurbaji A (2002) Molecular genetics of CYP2D6: clinical relevance with focus on psychotropic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 53:111–122
Zanger UM, Raimundo S, Eichelbaum M (2004) Cytochrome P450 2D6: overview and update on pharmacology, genetics, biochemistry. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 369:23–37
Shapiro DA, Renock S, Arrington E, Chiodo LA, Liu LX, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Mailman R (2003) Aripiprazole, a novel atypical antipsychotic drug with a unique and robust pharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1400–1411
Product information (2006) Abilify (Aripiprazole). Otsuka Pharmaceutical Europe, London
Molden E, Lunde H, Lunder N, Refsum H (2006) Pharmacokinetic variability of aripiprazole and the active metabolite dehydroaripiprazole in psychiatric patients. Ther Drug Monit 28:744–749
Rudberg I, Hendset M, Uthus LH, Molden E, Refsum H (2006) Heterozygous mutation in CYP2C19 significantly increases the concentration/dose ratio of racemic citalopram and escitalopram (S-citalopram). Ther Drug Monit 28:102–105
Schaeffeler E, Schwab M, Eichelbaum M, Zanger UM (2003) CYP2D6 genotyping strategy based on gene copy number determination by TaqMan real-time PCR. Hum Mutat 22:476–485
Kane JM, Carson WH, Saha AR, McQuade RD, Ingenito GG, Zimbroff DL, Ali MW (2002) Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole and haloperidol versus placebo in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 63:763–771
Potkin SG, Saha AR, Kujawa MJ, Carson WH, Ali M, Stock E, Stringfellow J, Ingenito G, Marder SR (2003) Aripiprazole, an antipsychotic with a novel mechanism of action, and risperidone vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:681–690
Marder SR, McQuade RD, Stock E, Kaplita S, Marcus R, Safferman AZ, Saha A, Ali M, Iwamoto T (2003) Aripiprazole in the treatment of schizophrenia: safety and tolerability in short-term, placebo-controlled trials. Schizophr Res 61:123–136
Ramaswamy S, Vijay D, William M, Sattar SP, Praveen F, Petty F (2004) Aripiprazole possibly worsens psychosis. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 19:45–48
Oosterhuis M, Van De KG, Tenback D (2007) Safety of aripiprazole: high serum levels in a CYP2D6 mutated patient. Am J Psychiatry 164:175
Hendset M, Haslemo T, Rudberg I, Refsum H, Molden E (2006) The complexity of active metabolites in therapeutic drug monitoring of psychotropic drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 39:121–127
de Leon J, Susce MT, Pan RM, Fairchild M, Koch WH, Wedlund PJ (2005) The CYP2D6 poor metabolizer phenotype may be associated with risperidone adverse drug reactions and discontinuation. J Clin Psychiatry 66:15–27
Kohnke MD, Griese EU, Stosser D, Gaertner I, Barth G (2002) Cytochrome P450 2D6 deficiency and its clinical relevance in a patient treated with risperidone. Pharmacopsychiatry 35:116–118
Huang ML, Van PA, Woestenborghs R, De CR, Heykants J, Jansen AA, Zylicz Z, Visscher HW, Jonkman JH (1993) Pharmacokinetics of the novel antipsychotic agent risperi1done and the prolactin response in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 54:257–268
Kubo M, Koue T, Inaba A, Takeda H, Maune H, Fukuda T, Azuma J (2005) Influence of itraconazole co-administration and CYP2D6 genotype on the pharmacokinetics of the new antipsychotic ARIPIPRAZOLE. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20:55–64
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hendset, M., Hermann, M., Lunde, H. et al. Impact of the CYP2D6 genotype on steady-state serum concentrations of aripiprazole and dehydroaripiprazole. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63, 1147–1151 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0373-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-007-0373-6