Article Text
Statistics from Altmetric.com
On 25 January 2021, a special restaurant named the ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ was opened in a prime locality of Shanghai, China; it emerged from a popular publicly broadcast welfare TV programme of the same name.1 This restaurant’s waiters are older patients with cognitive impairment, and the cumulative number of views for the programme has now exceeded 1.4 billion online.2 3 After the show was broadcast for two consecutive years, the filming party decided to open the restaurant officially, and the waiting duties were assumed by older people living with disability and dementia. The restaurant’s goal is to change Chinese society’s inherent views on the issues of disability and dementia and to remind the public to focus on a series of issues including the reintegration of older people living with disability and dementia to re-serve others and to rebuild public evaluations regarding them.
By the end of 2019, in China, the number of older people living with disability and dementia reached 50 million.4 Figure 1 shows the prevalence of disability for activities of daily living among Chinese people aged 60 years and above.4 Studies have also specifically pointed out that, among all the ways to help groups with disability and dementia, providing job opportunities, continuing education opportunities and even providing art exhibition opportunities are the most important.5 6 Many people believe that once a person is affected by disability and dementia, all their social functions will be lost, and they will never be able to return to society.7 This view, which is propagated by society as well as families, tends to create dislike, discrimination and abandonment towards older people who are living with disability and dementia; it also causes very poor self-worth among them.8
The prevalence of disability for activities of daily living in Chinese elderly aged 60 years and above.4
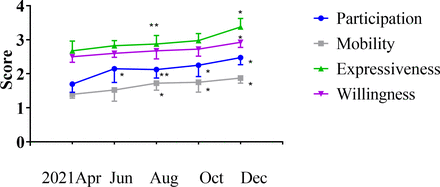
The opening of the ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ is a pioneering initiative. Currently, nearly 10 older people living with disability and dementia are working in this restaurant, and they remain mainly in charge of ordering and serving. Figure 2 shows how these special waiters’ social service communication activities, including willingness to participate, activity participation, language expression and mobility, have been improved over 8 months after they began to engage in providing restaurant services. Meanwhile, the ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ has set up and organised a popular science corner, a talking phone booth and regular popular science salons, which have changed the restaurant into a carnival of ‘love’ and ‘popular science’. Furthermore, this restaurant has an ‘Overlord Clause’: only people aged over 60 years can make an appointment for dinner.9 This clause thus aims to aid the elderly in finding their self-worth and in enjoying social attention.
The improvement of the social service communication activities of the elderly waiters in the ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’. *p<0.05 (compared with baseline (April 2021)); **p<0.01 (compared with baseline (April 2021)).
The ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ has been in operation for nearly 1 year. However, with its operation, new difficulties have gradually emerged. Can the restaurant be self-sufficient amid the fierce market competition of the metropolis? Do such non-profit restaurants require government support? Are complete and unobstructed emergency plans and relief channels available for older restaurant workers living with disability and dementia? Most importantly, how can we protect the elderly from becoming ‘stars’ that can be manipulated by businesses or placed in demand by the public? Towards this end, the ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ has organised an expert team on health protection and a team of college-student volunteers; furthermore, it has established an evaluation mechanism for the entry and exit of the elderly. Taking the help of the domestic medical think tank ‘Da Yi Xiao Hu’, the restaurant has become the ‘Great Health Project Management Demonstration Base’10 and is treated as a classic case of China’s big health cause for studying, analysing and searching for a systematic solution to the issues of older people living with disability and dementia and their need to return to society. The ‘Unforgettable Restaurant’ serves as an opportunity to encourage older people who are living with disability and dementia to speak up for themselves and take the first step towards returning to society by serving others.11
Note: The assessment of the social service communication activities for this study’s elderly uses a questionnaire that has been optimised based on literature regarding the senile cognitive impairment, social services and social communication of the elderly.12–14 A total of six parts were included in the questionnaire: willingness to attend activities, attention in activities, expression ability, ability to communicate with others, degree of participation and enjoyment of the process of activities. The elderly waiters’ performances in the activities were quantitatively evaluated by trained staff using a questionnaire. The data were issued, collected and filled out by specially trained and qualified staff. All data entries were reviewed by a dedicated designated member of the research team to ensure the accuracy of the findings.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Shanghai Mental Health Center (IORG Number: IORG0002202, FWA Number: FWA00003065). The Institutional Ethics Committee, Shanghai Mental Health Center also approved the consent procedure. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
Dr Ping Jiang obtained her PhD from the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, the Second Military University, China in 2005. She is currently a researcher at the Department of Biochemistry and Psychopharmacology, Shanghai Mental Health Center, China, where she has worked since 2010. Her main research interests include medical communication and TDM of antipsychotic.

Dr Ting Xu obtained her PhD from the Department of Hospital Management, Antai College of Economics and Management, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China in 2015. She is currently an assistant professor at the Department of Nursing Innovation and Entrepreneurship, School of Nursing and Health Management, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, China, where she has worked since 2018. She is also the leader of Project ‘Volunteer at the “Unforgettable Restaurant” Great Health Project Management Demonstration Base’. Her main research interests include aged care and emergency management.

Footnotes
PJ and TX contributed equally as the co-first authors
Contributors PJ, JHC and TW participated in the design of the article. PJ, TX, CZ, JHC and TW were involved in the induction and summary of meaning. TX collected the data, PJ drafted the manuscript and all authors revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. The authors are responsible for the paper’s data.
Funding This work was supported by National Social Science Fund Project (18BGL242); Project of the Key Discipline Construction, 3-Year Initiative Plan for Public Health Action in Shanghai(GWV-10.1-XK18, GWV-10.1-XK21); Teacher Train and Progress Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (JFXM201808); Shanghai Mental Health Center Project (2018-YJ-16); China Hospital Development Research Institute Hospital Management Construction Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (CHDI-2018-A-23); Shanghai Jiao Tong University Translational Medicine Interdisciplinary Research Fund (ZH2018QNB18); Young and Middle-aged Teachers Study Abroad Programme of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine; Wang Kuancheng Medical Award Fund Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University; Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences Project (SSF-21-02-13).
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.